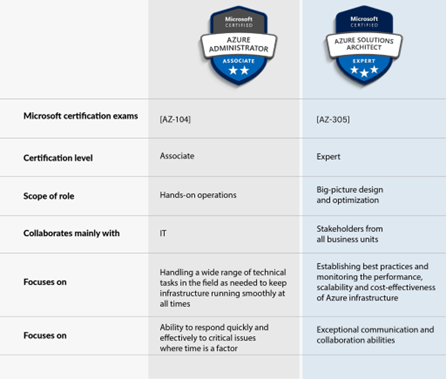
-
Network Team
Security and Access Management:
Network teams need to familiarise themselves with cloud-native security practices, including the implementation of network security groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic to Azure resources. Additionally, understanding role-based access control (RBAC) is essential for managing permissions effectively.
Hybrid Network Integration:
As many businesses operate in hybrid environments, network teams need skills in establishing secure, low-latency connections. This includes configuring VPNs and Azure ExpressRoute to create seamless links between on-premises networks and the cloud.
Network Monitoring and Optimisation:
To ensure optimal performance, network teams should leverage cloud-native tools such as Azure Monitor and Azure Network Watcher. These tools provide insights into network performance, enabling teams to monitor traffic, diagnose issues, and optimise configurations. By analysing metrics and logs, network professionals can identify bottlenecks and make data-driven decisions to enhance reliability and speed.
-
Database Team
Migration Strategies:
Transitioning to the cloud requires careful planning for database migration. Database teams should develop a comprehensive migration strategy that assesses current on-premises databases and identifies the best cloud-managed services. This includes evaluating potential downtime and implementing solutions like Azure Database Migration Service to minimise disruptions during the transition.
Scalability and High Availability:
Database teams must become proficient in features like automatic scaling, which allows resources to adjust based on demand, and replication, which ensures data is duplicated across multiple locations for redundancy. Additionally, teams should explore database sharding techniques to improve performance by distributing data across multiple databases, thereby reducing load on individual resources.
Performance Tuning in Cloud:
Database professionals should familiarise themselves with cloud-native features such as indexing and caching to enhance query performance. Furthermore, leveraging in-memory databases can significantly speed up data retrieval processes. Continuous monitoring and optimisation practices should be implemented to ensure applications run efficiently and users have quick access to data.
-
Data Team
Cloud Data Integration:
With the increasing volume of data generated, data teams must become proficient with cloud-native ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools, such as Azure Data Factory. These tools enable the seamless movement and orchestration of data across different sources, facilitating efficient data integration. Mastery of these technologies is essential for creating reliable and scalable data pipelines that support analytics and business intelligence activities.
Big Data and Analytics:
Data teams should leverage cloud-native analytics tools like Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Databricks to build scalable data processing workflows. These platforms allow teams to analyse large volumes of data, enabling advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities. Understanding how to structure and manage data for analysis will be key to deriving insights that drive decision-making.
Data Security and Compliance:
Data teams must implement encryption strategies to protect data both at rest and in transit. Additionally, familiarity with compliance standards, such as GDPR, is essential to ensure that data handling practices meet legal requirements. Teams should develop governance policies that address data security, access controls, and auditing to maintain compliance and protect organisational assets.